
- #Tax act s corp plus#
- #Tax act s corp free#
The S corporation is the only business tax status that lets you save on Social Security and Medicare taxes while avoiding double taxation.
#Tax act s corp plus#
Then you might owe self-employment tax plus penalty and interest on those. audits And, if the IRS determines you aren’t paying yourself a reasonable salary, it may reclassify some dividends as earnings. S corporations are also somewhat more prone to IRS. So the more you take in dividends, the less you can put into a tax-advantaged plan. Meanwhile, earnings determine caps on annual IRA or other retirement plan contributions. However, the paperwork burden is lighter than for C corporations. S corporations have extra recordkeeping and meeting requirements compared to sole proprietorships. There are also extra administrative costs. These restrictions can prevent an S corporation from attracting investors. Plus, they can only have a single class of shareholders. residents, can choose S corporation status. corporations with no more than 100 owners, all of whom are U.S. First, not all LLCs are eligible for S corporation status. What Are the Disadvantages of Being an S Corporation?ĭespite the potential benefits, S corporation status for an LLC isn’t a no-brainer.
Then file a Form 2553 to elect an S corporation tax structure. This causes the business to be taxed as a C corporation. File a Form 8832, Entity Classification Election. An LLC with more than one member will default to partnership status.Īn LLC can choose to be treated as an S corporation in a two-step process:. A single-member LLC will by default be treated as a sole proprietor by the IRS. If the LLC doesn’t choose, the IRS applies a default tax structure depending on the number of members of the LLC. Meanwhile, S corp describes how the IRS treats a business for tax purposes. These potential tax benefits are the main reason LLCs elect to be taxed as S corporations.Īn LLC can choose an S corporation tax structure because an LLC is a business entity defined by state law. This can produce additional tax savings not available to C corporations. Then you’d owe just $7,650 in self-employment tax, for a tax savings of $7,650.Īnother potential advantage of an S corporation is that the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act made certain pass-through businesses eligible for a 20% Qualified Business Income deduction. If you have elected be taxed as an S corporation, you might have $50,000 pass through as earnings and $50,000 distributed as dividends. In addition to income taxes, you’ll owe self-employment tax of $15,300, or 15.3%. All $100,000 will pass through to you as self-employment income. 
Say you are sole member of an LLC that earns $100,000 in net income. How an LLC Being Taxed as an S Corp Works
#Tax act s corp free#
Meanwhile, other profits pay out as dividends that are free of self-employment tax.īy having LLC treated as an S Corp for tax purposes, a business owner may save a considerable amount in tax payments.
The owner of an S corporation can let some of their business profits pass through as earnings. That means dividend recipients don’t have to pay Social Security and Medicare taxes on that income. Income from a corporation is treated as a dividend rather than earnings. There are two more key factors to consider here: That’s because employers pay another 6.2% for Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare without passing it onto employees. As a result, employees withhold just 6.2% for Social Security and 1.45% for Medicare. The self-employment tax comes to 15.3%, with Social Security representing 12.4% and Medicare tax representing 2.9%.Īs anyone who’s checked their pay stub knows, self-employment taxes are higher than Social Security and Medicare taxes paid by workers who aren’t self-employed. When income from LLCs passes through to owners, they pay tax on it as self-employment income. 
When an LLC opts for an S corporation tax structure, it typically changes the way the IRS treats that LLC’s income.
Minimizing paperwork and overhead: Compared to a regular corporation, an LLC has fewer record-keeping and meeting requirements. 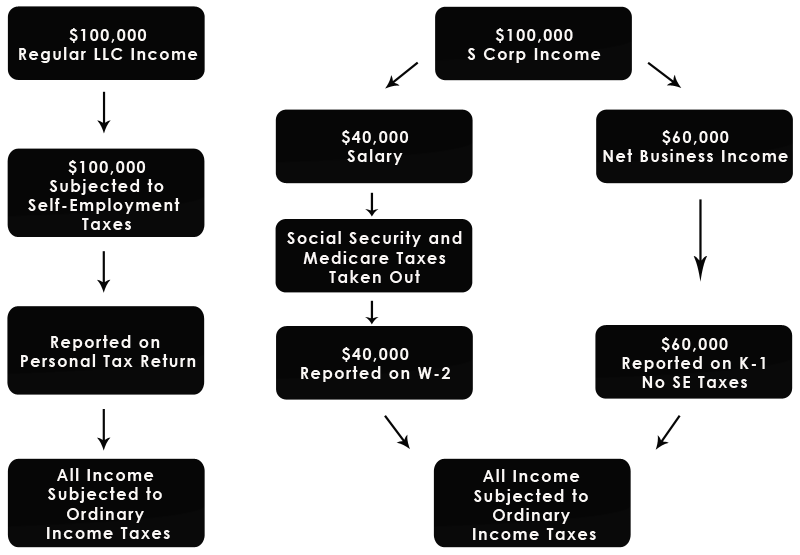
Its income passes straight to the owners as self-employment income, avoiding corporate income tax.
 Avoiding double taxation: An LLC is basically a pass-through entity. Partnership owners and sole proprietors may be personally liable for all business debts. Typically, liability is no more than the amount each invested in the business. Limiting liability: LLC owners have limited personal liability for debts owed by the business. The LLC business entity has some appealing advantages over its alternatives.
Avoiding double taxation: An LLC is basically a pass-through entity. Partnership owners and sole proprietors may be personally liable for all business debts. Typically, liability is no more than the amount each invested in the business. Limiting liability: LLC owners have limited personal liability for debts owed by the business. The LLC business entity has some appealing advantages over its alternatives.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
